Examples¶
Kernel Polynomial Method (Chebyshev Polynomial expansion)¶
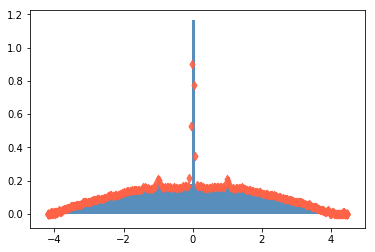
The Kernel Polynomial Method can estimate the spectral density of large sparse Hermitan matrices with a low computational cost. This method combines three key ingredients: the Chebyshev expansion + the stochastic trace estimator + kernel smoothing.
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
n = 3000
g = nx.erdos_renyi_graph(n , 3/n)
W = nx.adjacency_matrix(g)
vals = np.linalg.eigvals(W.todense()).real
from emate.hermitian import tfkpm
num_moments = 300
num_vecs = 200
extra_points = 10
ek, rho = tfkpm(W, num_moments, num_vecs, extra_points)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(vals, density=True, bins=100, alpha=.9, color="steelblue")
plt.scatter(ek, rho, c="tomato", zorder=999, alpha=0.9, marker="d")
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.show()
References¶
[1] Wang, L.W., 1994. Calculating the density of states and optical-absorption spectra of large quantum systems by the plane-wave moments method. Physical Review B, 49(15), p.10154.
[2] Hutchinson, M.F., 1990. A stochastic estimator of the trace of the influence matrix for laplacian smoothing splines. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation, 19(2), pp.433-450.
Sthocastic Lanczos Quadrature¶
Given a semi-positive definite matrix \(A \in \mathbb R^{|V|\times|V|}\), which has the set of eigenvalues given by \(\{\lambda_i\}\) a trace of a matrix function is given by
The methods for calculating such traces functions have a cubic computational complexity lower bound, \(O(|V|^3)\). Therefore, it is not feasible for large networks. One way to overcome such computational complexity it is use stochastic approximations combined with a mryiad of another methods to get the results with enough accuracy and with a small computational cost. The methods available in this module uses the Sthocastic Lanczos Quadrature, a procedure proposed in the work made by Ubaru, S. et.al. [1] (you need to cite them).
Estrada Index¶
import scipy
import scipy.sparse
import numpy as np
from emate.symmetric.slq import pyslq
import tensorflow as tf
def trace_function(eig_vals):
return tf.exp(eig_vals)
num_vecs = 100
num_steps = 50
approximated_estrada_index, _ = pyslq(L_sparse, num_vecs, num_steps, trace_function)
exact_estrada_index = np.sum(np.exp(vals_laplacian))
approximated_estrada_index, exact_estrada_index
The above code returns
(3058.012, 3063.16457163222)
References¶
1 - Ubaru, S., Chen, J., & Saad, Y. (2017). Fast Estimation of tr(f(A)) via Stochastic Lanczos Quadrature. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 38(4), 1075-1099.
2 - Hutchinson, M. F. (1990). A stochastic estimator of the trace of the influence matrix for laplacian smoothing splines. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation, 19(2), 433-450.